In-Depth: What Does ‘Fine Watchmaking’ Really Mean (And Can I Tell When I See It)?
“You were supposed to get a good tree. Can’t you even tell a good tree from a poor tree?” – Lucy Van Pelt, A Charlie Brown Christmas
For anyone getting interested in watches for the first time – interested in watches as watches, not just as incidental objects for telling the time – the natural first question is, how do you tell a good watch from the merely mediocre or the downright terrible? The question can be very baffling, and even more so the more you find out about watches.
Wristwatches exist today, even if you leave inexpensive quartz out of the equation, in what seems an almost infinite range of prices and quality. We assume that as the price goes up, quality goes up as well, but what does that mean? Why is a steel, water-resistant automatic watch $500 from one manufacturer, and $25,000 from another?
It’s become fairly difficult, at this point in the history of the wristwatch, to find a genuinely bad watch. The basic technology behind the watch has been undergoing a process of progressive refinement for about five hundred years and we humans have gotten very, very good at making them. The simple answer to the question is that a watch is a good watch if it’s reliable, durable and accurate, and offers fit, finish, and performance that make sense for what you paid. A more interesting way to frame the question is to think about why some watches from some manufacturers have generally been thought of as finer than watches from other manufacturers.
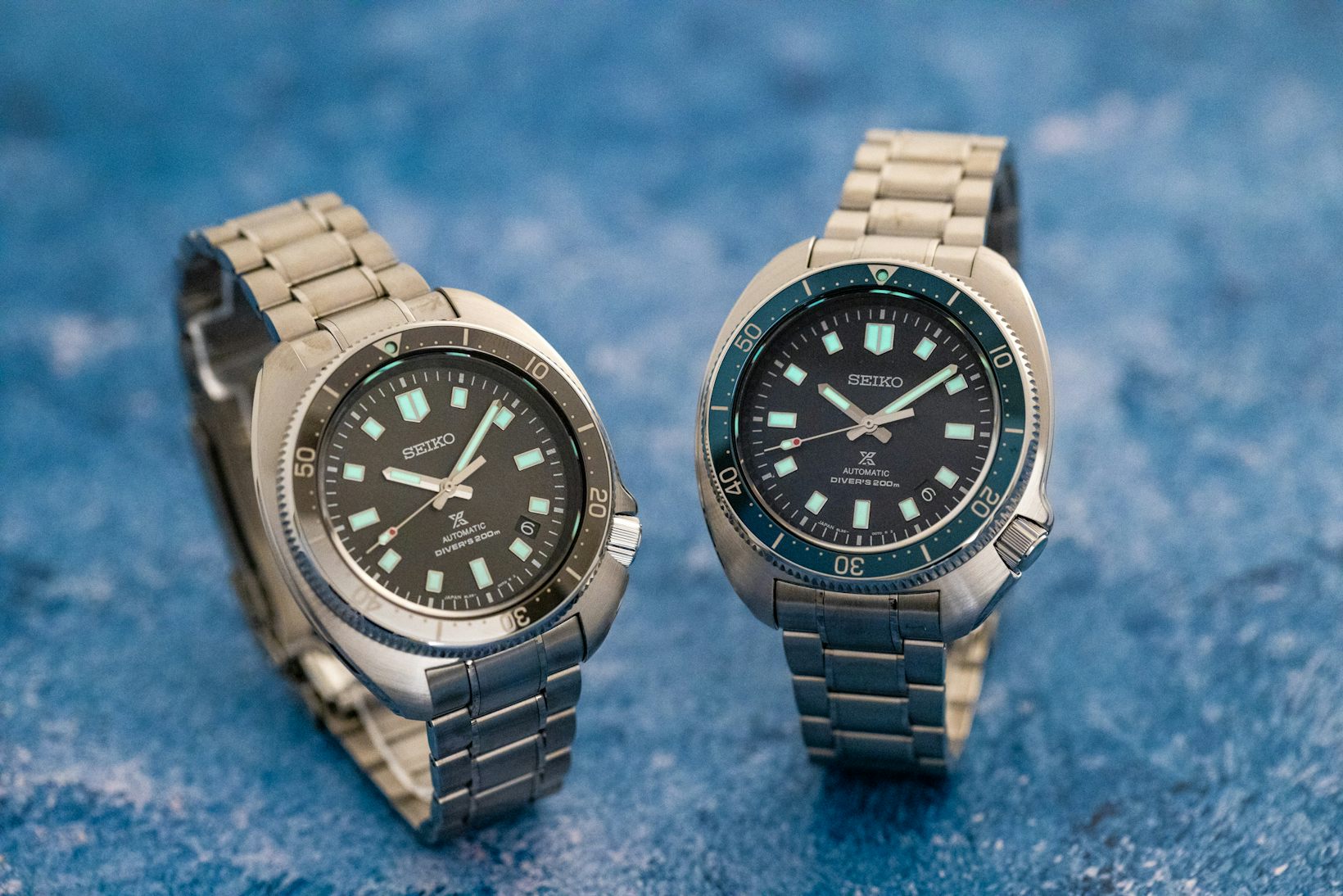
Here I want to emphasize again that fine watchmaking is not necessary to make a good watch, and a watch need not be an haute horlogerie achievement made by reclusive craftsmen in the Jura to be a good and even a great watch. Seiko, for instance, generally makes highly regarded watches that deliver a lot of bang for the buck; virtually everything Oris makes, likewise, is a great value, and so on. But while a Seiko Ice Diver or an Oris Big Crown Pointer Date are almost inarguably good watches (I say “almost” only because we all know watch enthusiasts really will argue about anything) nobody would call them examples of fine watchmaking, at least not in the traditional sense.
It’s also true that luxury watches and fine watchmaking aren’t necessarily synonymous. They can be, but whether or not a luxury watch is also an example of fine watchmaking depends on the amount of care, craft, and time that went into making the watch.
There are an enormous number of good watches out there, but there are vanishingly few really fine watches out there and just like anything else, there are standards for what constitutes fine watchmaking – we were kicking around the term haute horlogerie in the comments, not long ago and there was quite a lot of curiosity and confusion over it. Asking if a watch is a good watch, for me, has always meant asking what kind of watch it was intended to be, and how well it fulfills those intentions (a dive watch that’s hard to read may succeed as a postmodern piece of ironic commentary on the absurdity of the dive watch, but it’s a failure as a dive watch).
In a narrower sense, though, the fine-ness – haute-ness? – of a watch is evaluated by a set of standards that relate to one of the most often discussed but most difficult to evaluate aspects of watchmaking, which is finishing.
And here at last, we are on more solid ground. The standards for high-end movement finishing are somewhat dependent on the vocabulary of finishing a watchmaker uses – in English watchmaking, for instance, the types of decoration differ, sometimes dramatically, from the Swiss. But the standards themselves – in Swiss fine watchmaking, for instance – are for each type of decoration, well-established.
The highest standard for finishing is that it should be, as much as possible, done by hand. The partial or total absence of hand-finishing doesn’t mean an absence of hand work – watches with little or no hand-finishing often have at least some hand-work, and sometimes a lot of it, in assembly, quality control, and fine-tuning. Some brands have a lot of hand work in case polishing, or the dial furniture and hands, or in dial-making, but almost no hand-finishing in the movement. Nonetheless, good clean industrial movement finishing can produce a very handsome movement with all the immediate instinctive appeal you feel in the presence of precision machinery. But it’s not, per se, fine watchmaking.
Really top level hand-finishing is extremely hard to do. Also, it’s hard in a way that very few of us really understand. It requires a level of manual dexterity well outside anything that daily life usually demands of us. Certain kinds of surgery require a similar or higher degree of control – for instance, there’s a type of brain surgery used for tumors of the pituitary gland which involve tunneling in through the sphenoid bone in the nasal cavity – transsphenoidal surgery, which requires an apparently supernatural degree of physical coordination. Most of us, to put it mildly, are not neurosurgeons and so the opportunities for us to practice anything that requires really fine motor control are few and far between.
Unless you’ve been lucky enough to actually try hand-finishing as part of a brand workshop or factory visit (and botched it, which is of course the inevitable outcome of letting amateurs take their best shot) it’s almost impossible to understand just what it takes in terms of talent and training to pull it off. But if you spend even a little time wrapping your mind around just how tough it is to do really well, you start to appreciate the expert human touch that goes into fine hand-finishing.
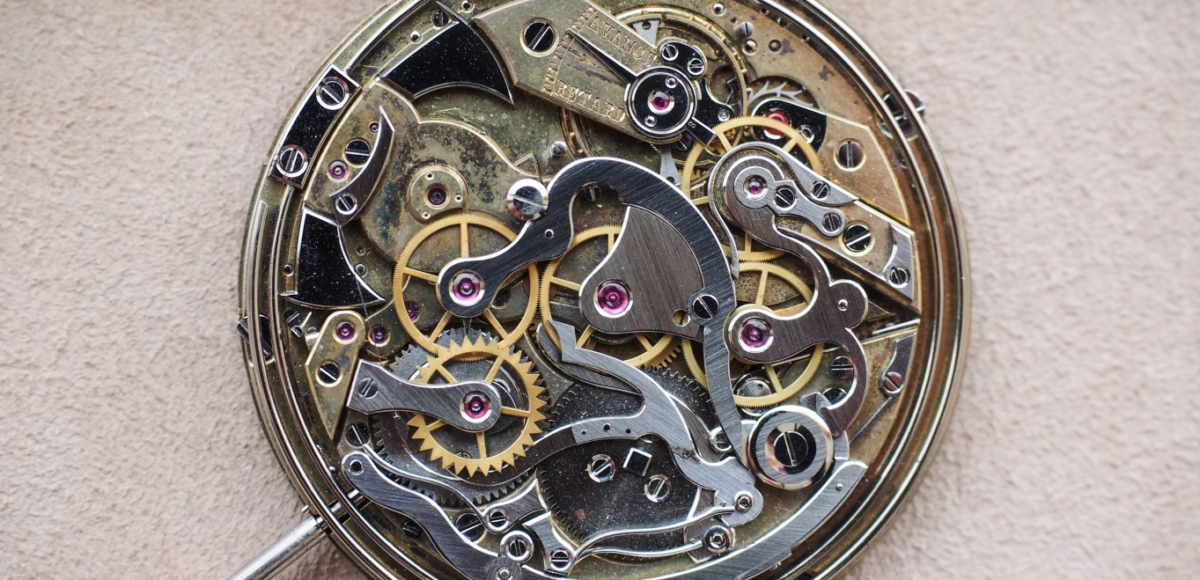
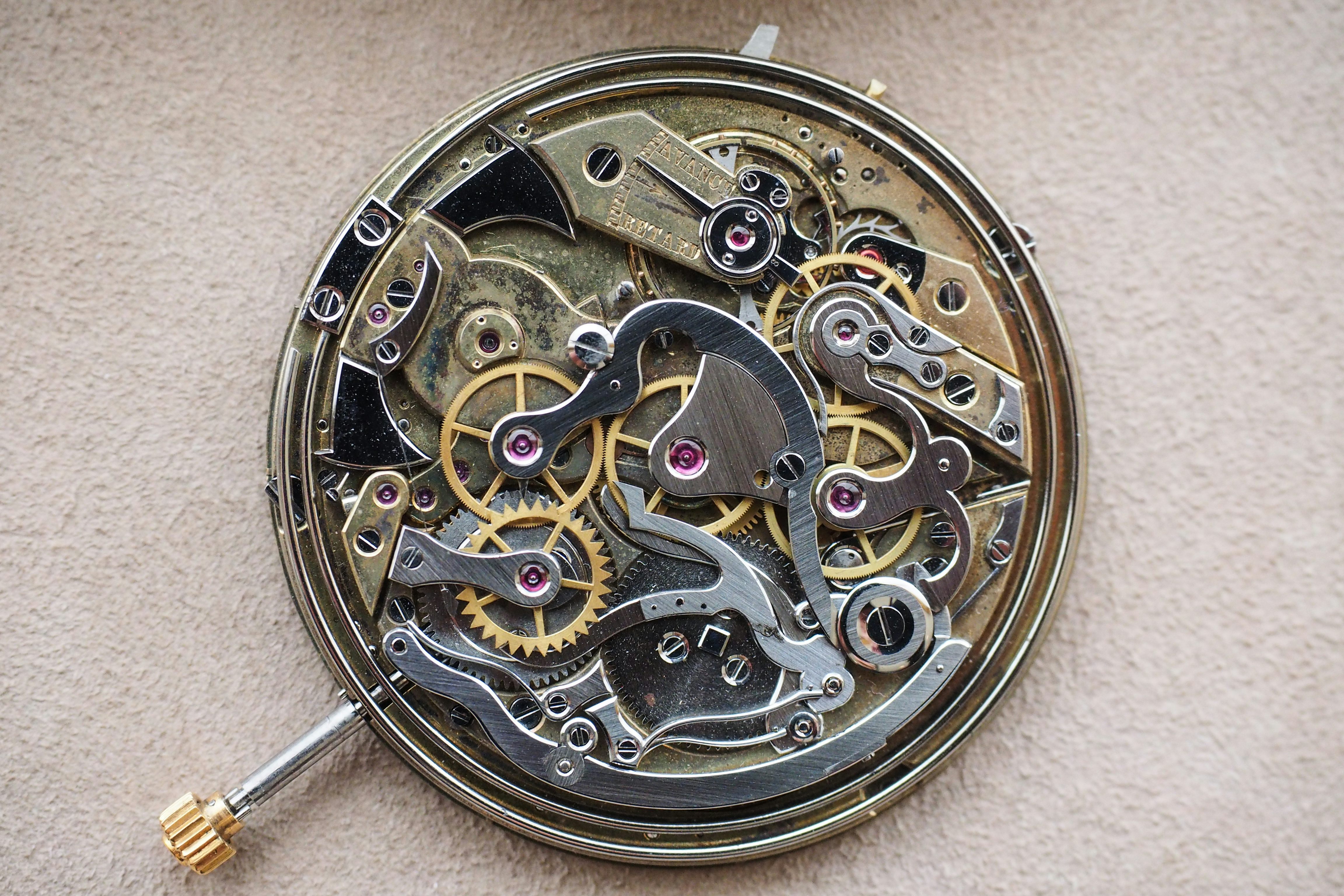
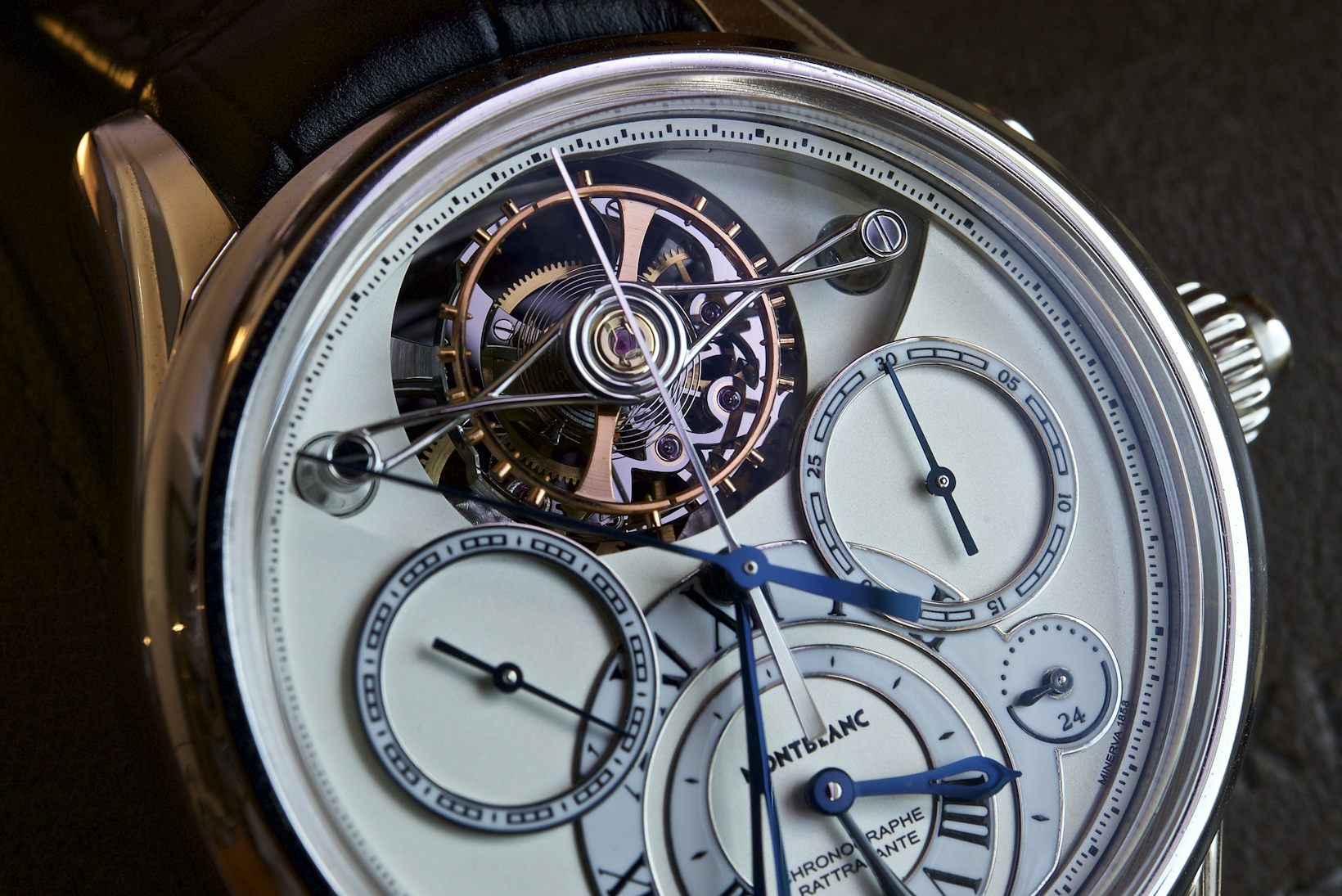
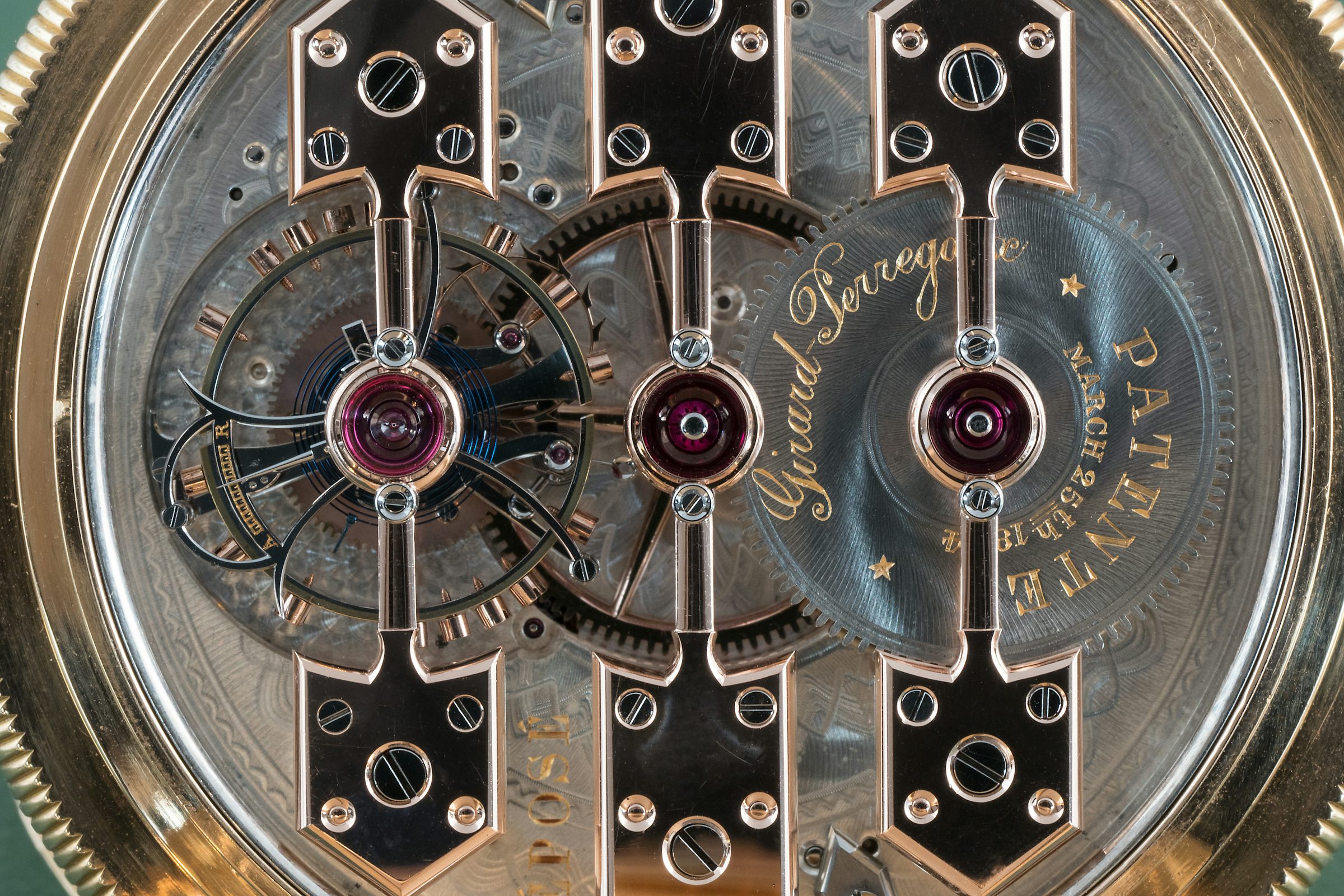
It’s difficult, therefore, to look at something like this Girard Perregaux observatory pocket watch and not feel slightly humbled. There was no such thing as automated finishing at the time this watch was completed (1889) and watches in this class were pretty much one-off masterpieces. Look at the absolutely huge, beautifully shaped and polished, and flawlessly set jewels in each bridge; the complex geometry of the bridges themselves; the laboriously unhurried and meticulous polishing of every individual screw, with black-polished heads; and above all, the gossamer thin tourbillon cage, beveled and black-polished, with inner corners so sharp you could cut yourself looking at them.
Kind of ruins you for anything else, no? This is the real standard – before industrialized luxury came along and made it possible for anyone to buy a pair of logo’d sunglasses from an international luxury conglomerate – for real haute horlogerie watchmaking.
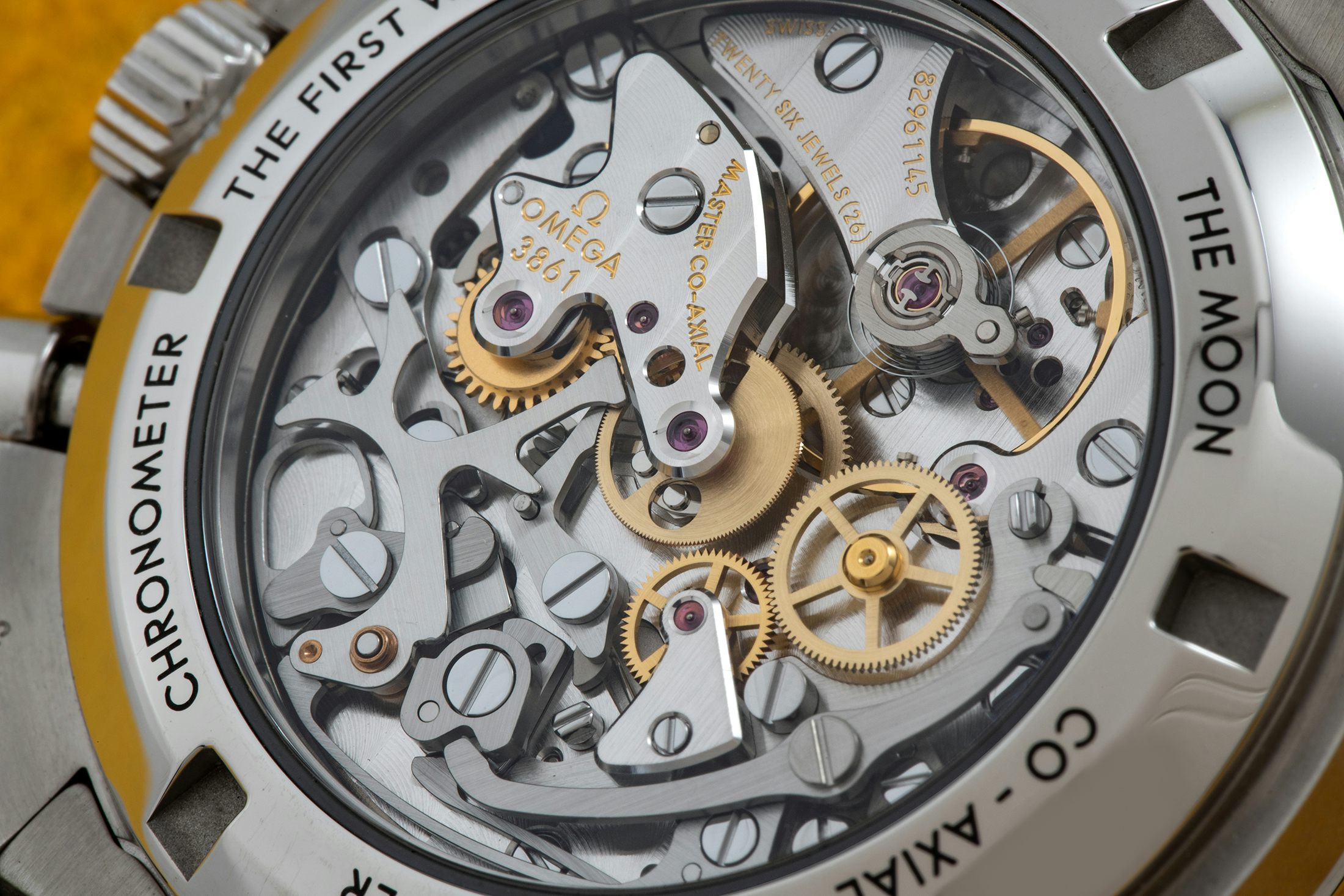
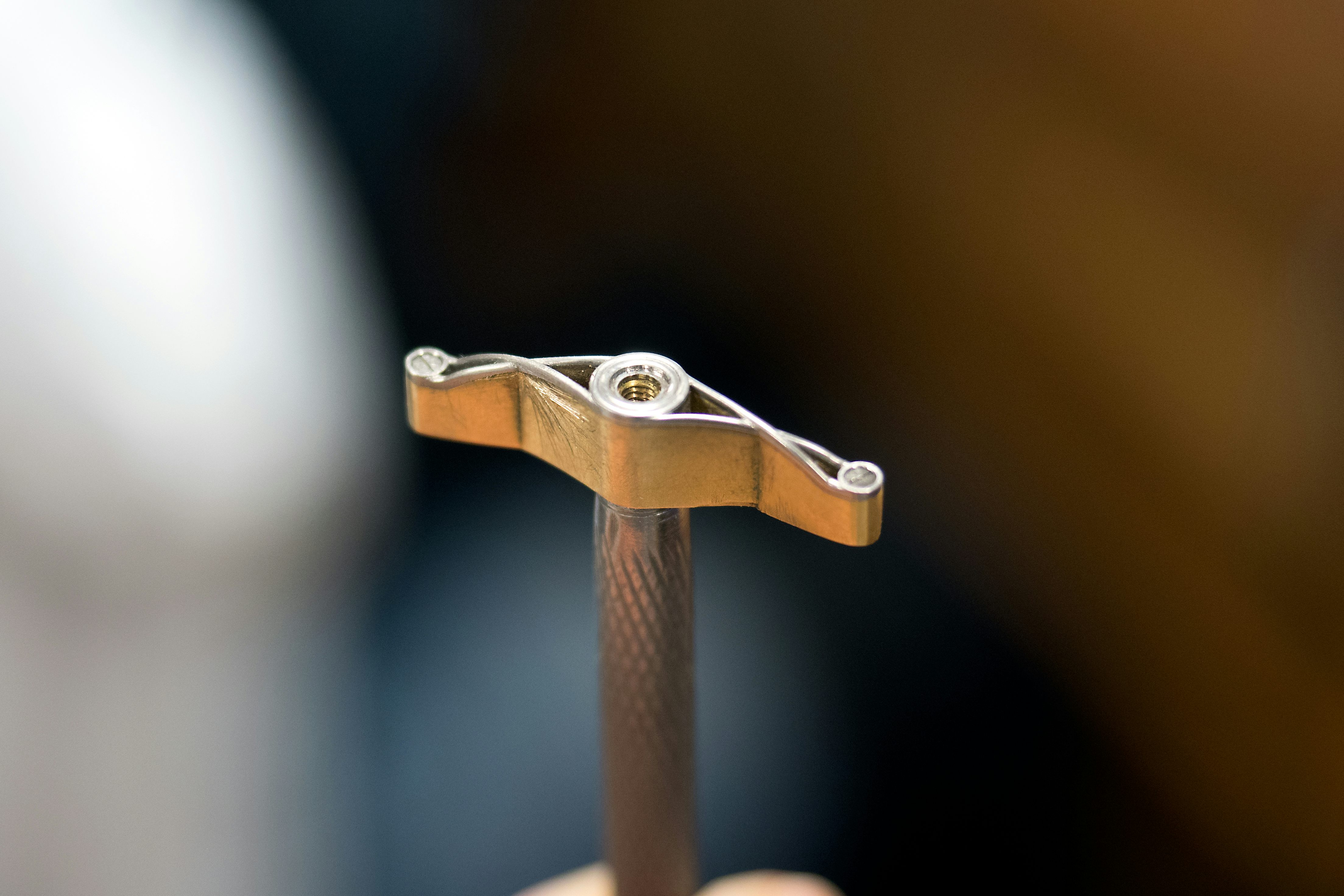
As an example, let’s look at chamfering, or anglage. This is a decorative technique that’s usually applied to the bridges of a movement, which are mostly made of rhodium-plated brass, and to some steel parts, as well. Anglage is the French word for chamfering, which means the creation of an angled transition between the upper surface and the flank – usually, a 45º angle, although some very high grade chamfering produces a rounded chamfer (as in the Dufour Simplicity). If you look up the difference between beveling and chamfering you’ll find that they do mean slightly different things but in practice the two are usually used interchangeably.
Now we come to the first essential point, which has to be made before we go any further: Every type of movement finishing can be done industrially, semi-industrially, or manually.
Manual finishing techniques sit at the top of the pecking order and it’s their presence or absence that determines whether or not a watch is an haute horlogerie watch.
The second essential point is that you can find examples of all three, mixed to varying degrees, in various watches, and even in the same watch.
Even from a single manufacturer, you can often find a combination of industrial finishing (automated) and partly industrial finishing (some hand work and some automated work) and sometimes, both combined with some final hand-finishing. Hand-finishing throughout, using traditional methods, is usually reserved for the top end of production.
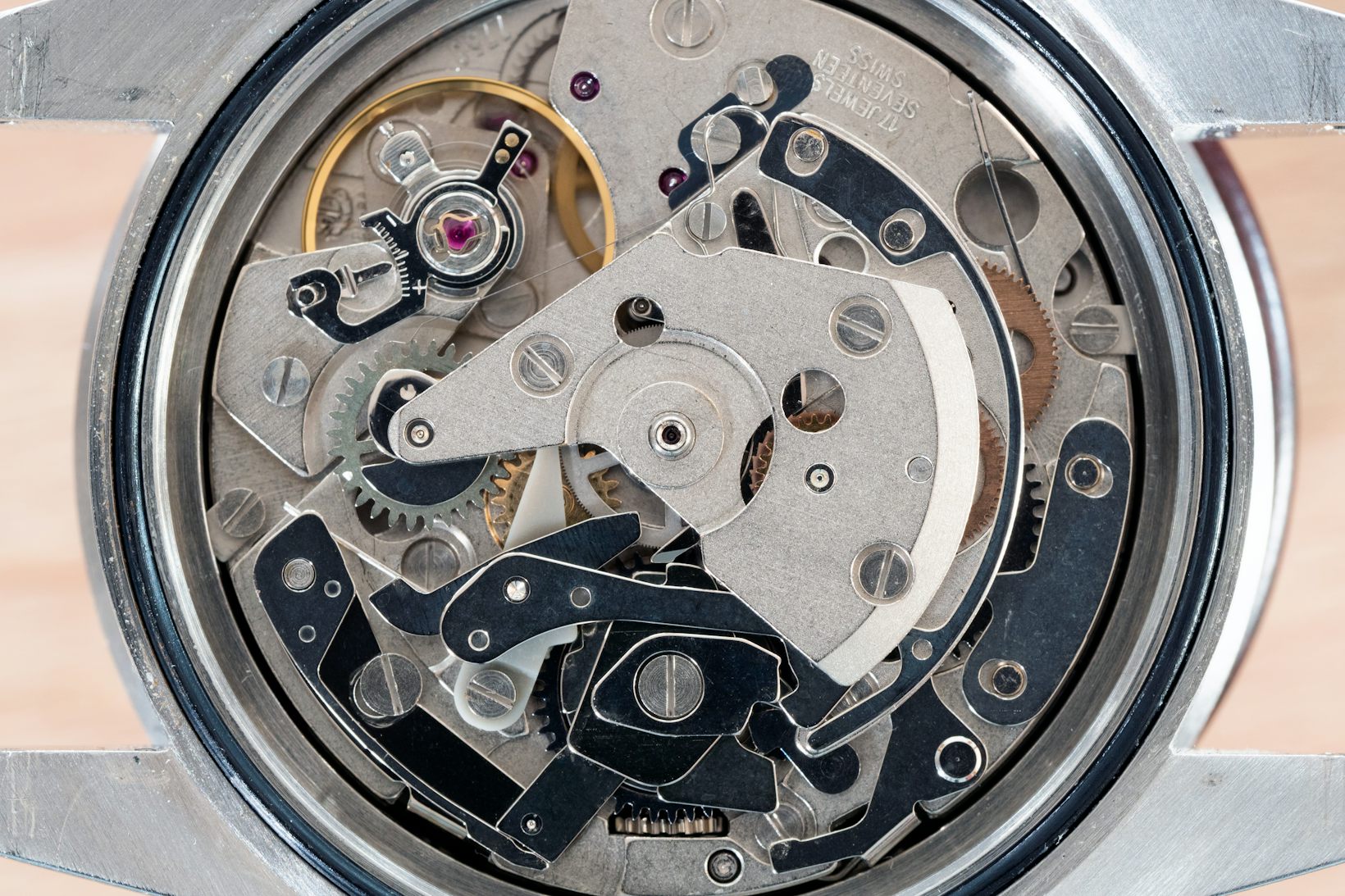
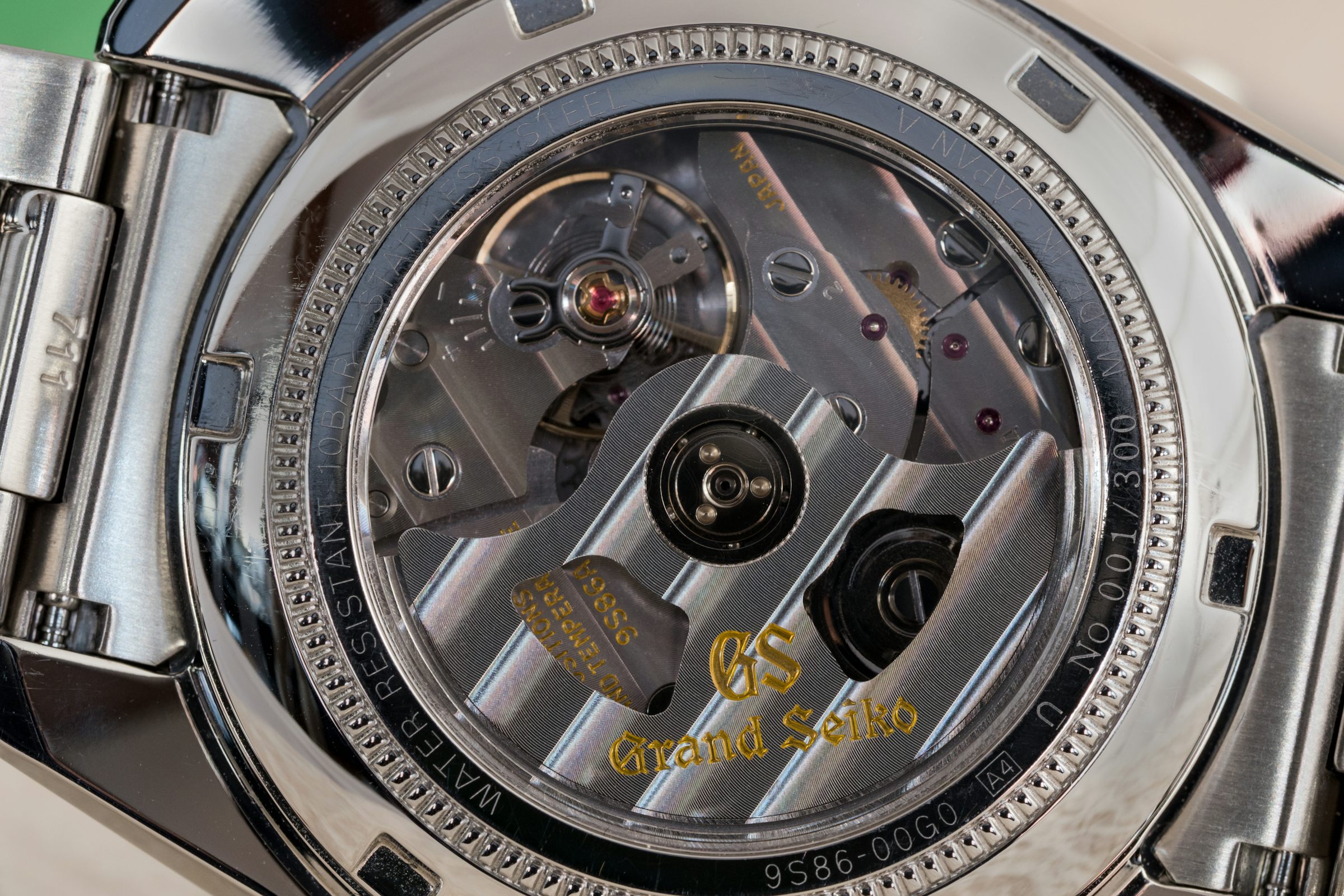
The simplest form of chamfering is the absence of any chamfering at all. The Grand Seiko Hi-Beat caliber 9S86, for instance, has no chamfering anywhere on the movement and the flat upper surface of the rotor, as well as the upper bridge and balance cock, simply form a very sharp, crisp 90º angle with the flank. The movement, however, presents a very clean, honest appearance and the fact that it was designed with reliability, durability, and precision as first priorities is immediately obvious. Compare it to the unfinished Valjoux/ETA 7750 movement up above, and you can see that there’s really no comparison at all.
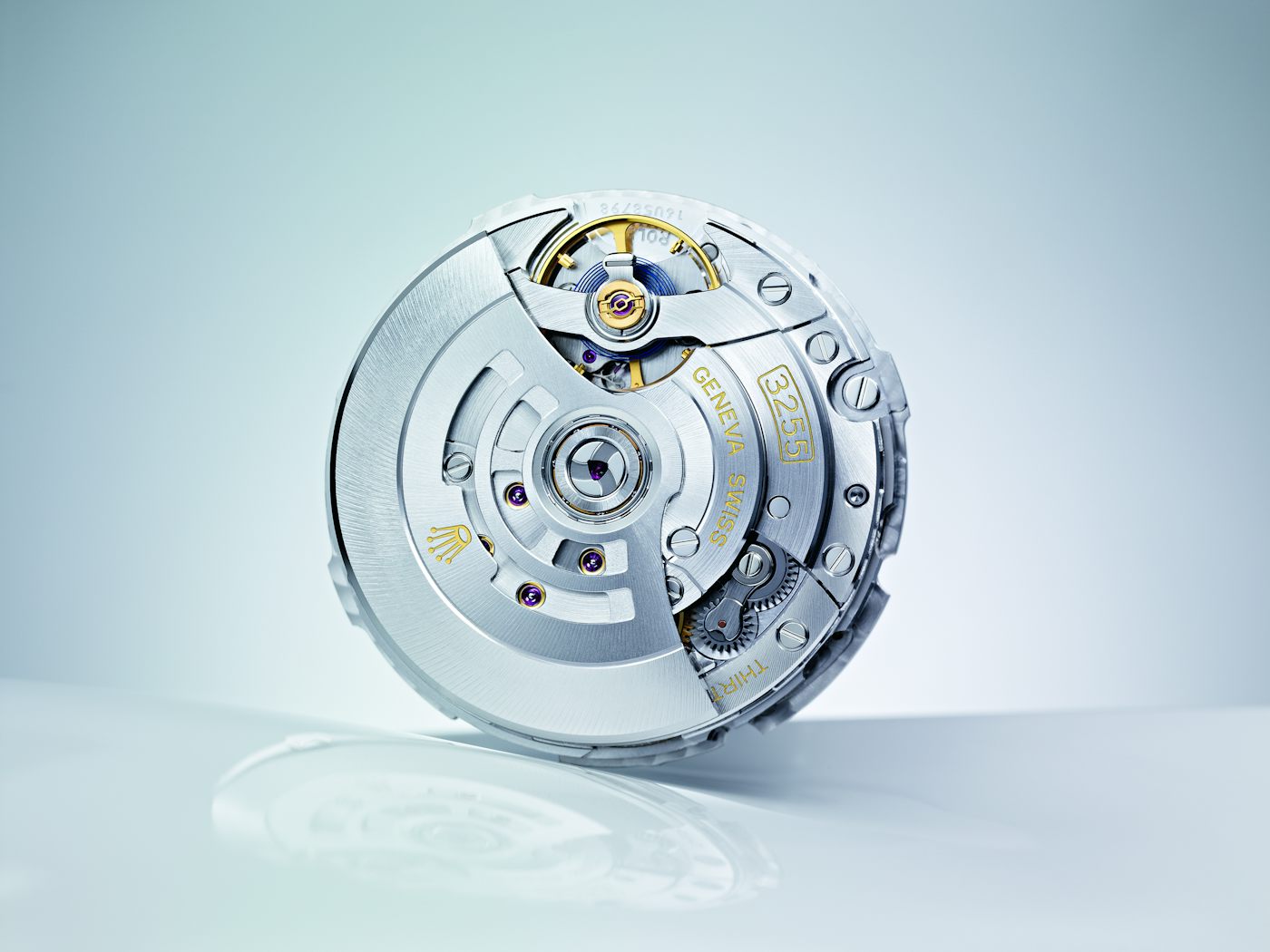
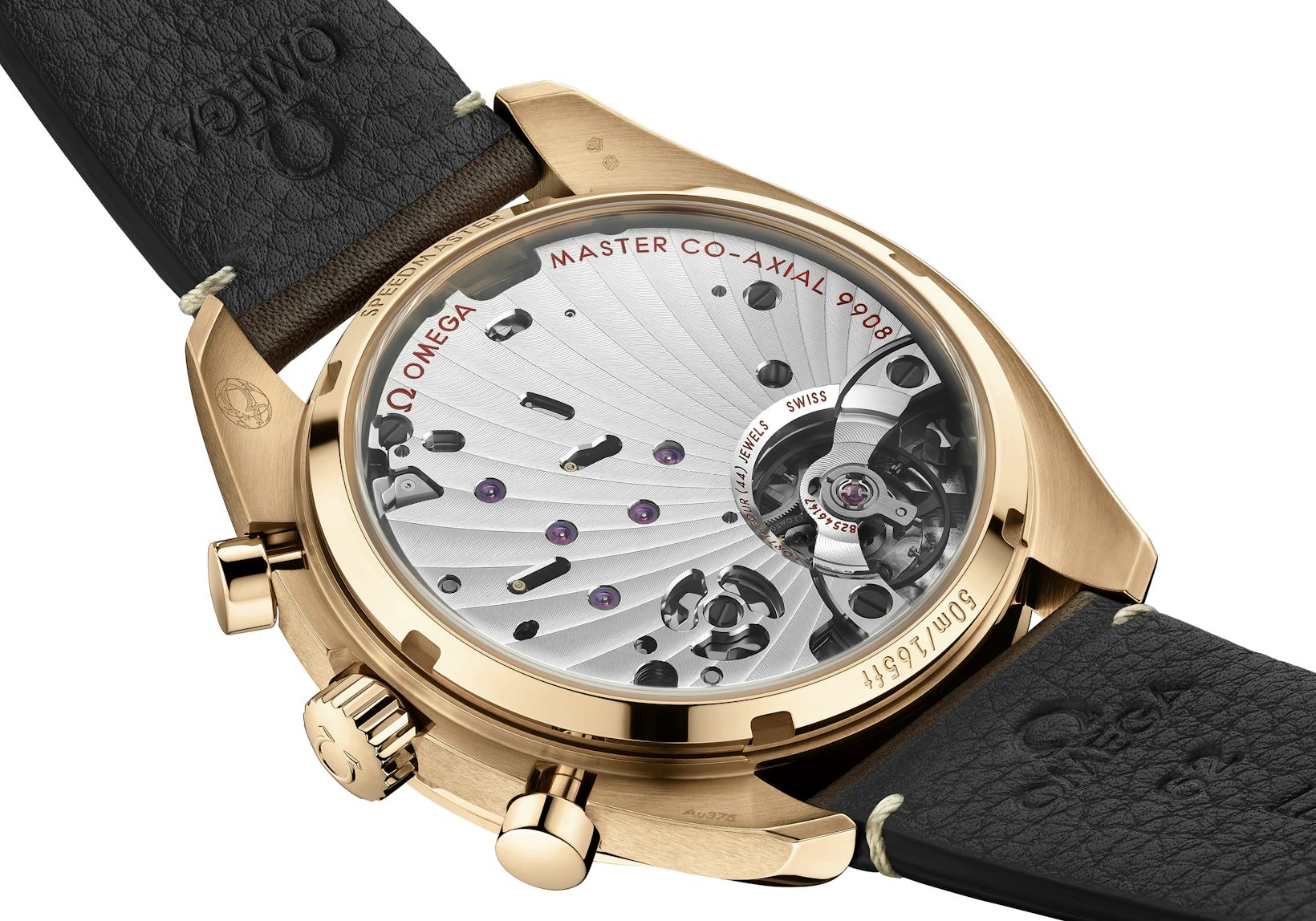
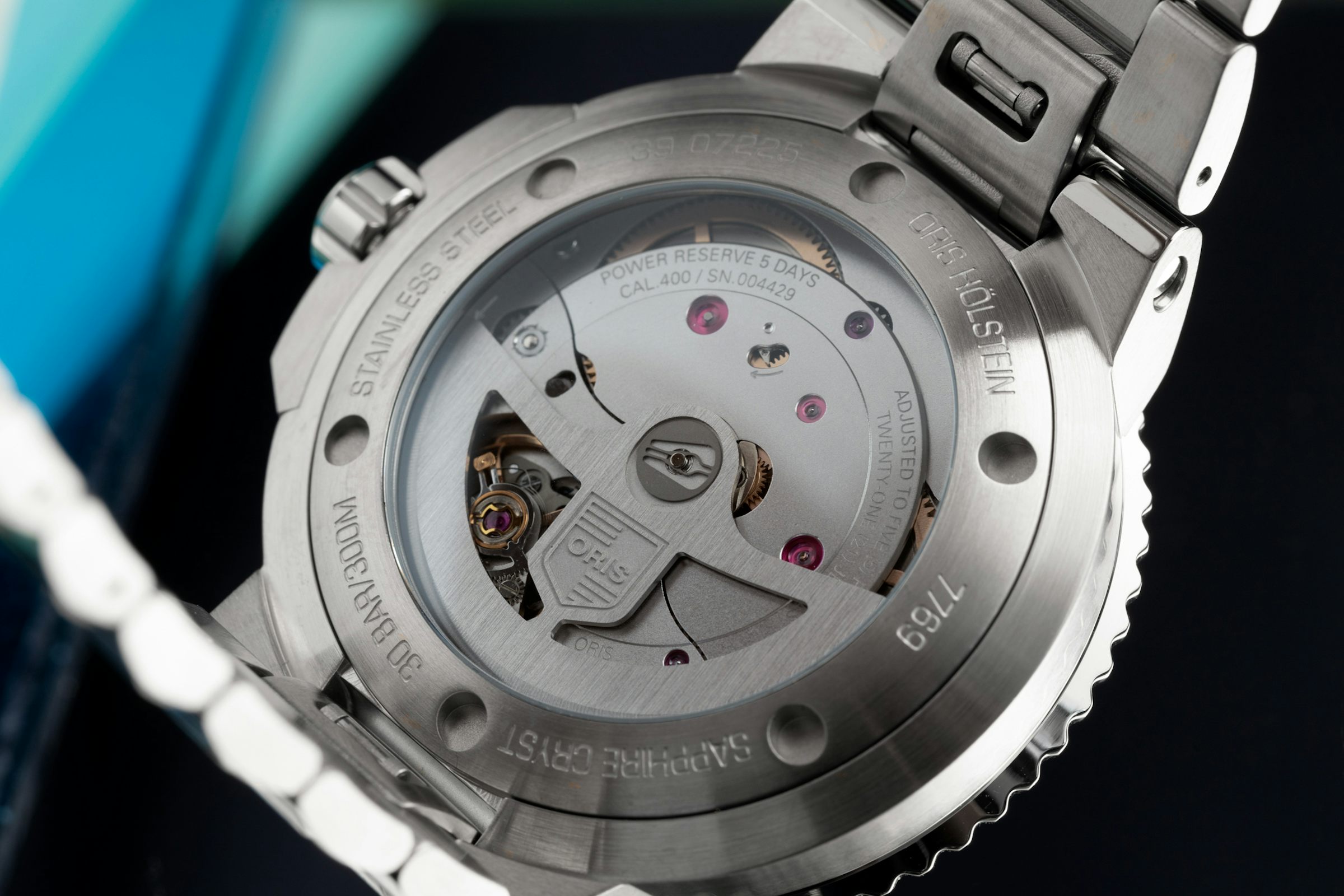
This is, with some differences in execution, the same approach taken by other brands doing industrial-level movement manufacturing, including Rolex, Omega, and Oris. You’ll notice that machine-executed finishing is not a single style, by the way; every company puts its own stamp (to make a weak pun) on their movements.
The next step up is to make the chamfers using either stamping or computer-guided milling tools. These methods can both produce visually satisfactory results and, in large series production, give you consistency across the entire production range in exchange for a fairly small increase in production time and complexity. This is relative, however, as every additional decorative finish means additional steps and depending on the degree of finishing applied, the extra time may be considerable.
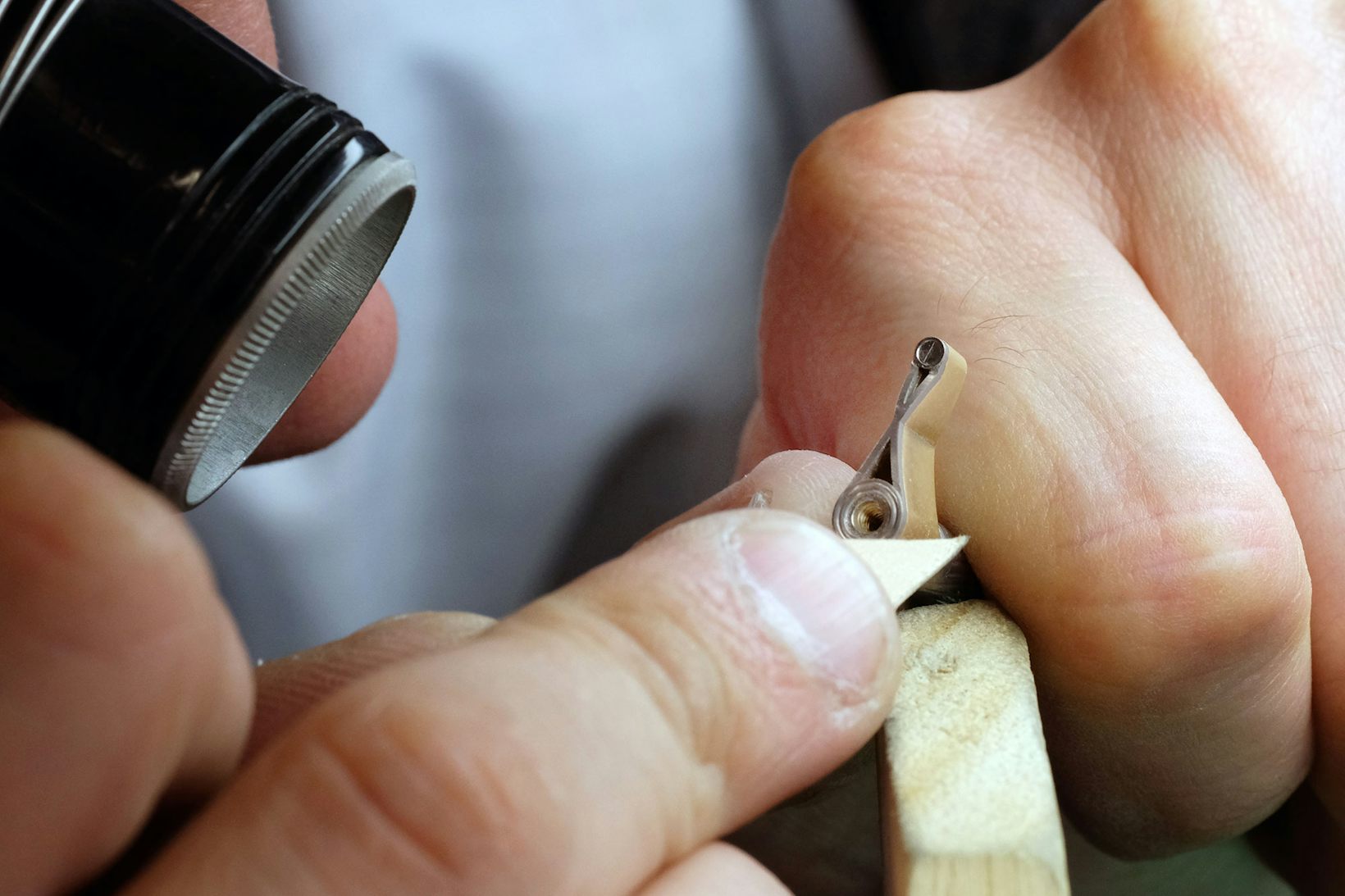
The haute horlogerie approach is another story. The really traditional way to do it is to take the bridge (for instance) and finish the flank (the vertical side of the part) and then form the chamfer using a file. The marks left by the file are then polished out with a stone polishing tool. The final polish is done using increasingly fine abrasives, and finished with a piece of pegwood covered in a diamond paste. The wood used is the woody pith of the gentian plant, which grows wild throughout Switzerland (the Swiss use it to make a schnapps that’ll burn the chrome off the bumper of a ’59 Caddy. If you’re having fondue in Switzerland and you’ve had enough fendant to think that a couple-three gentian schnapps are a good idea, don’t. Ask the man who knows.)
It’s been said (and written) that one of the hallmarks of hand-chamfering is the presence of sharp inner and outer corners, which CNC machines or stamping can’t duplicate, and as far as I know, this is still true.
You’re probably beginning to suspect by now that there is not a whole lot of start-to-finish hand-done chamfering in modern watchmaking, and you’d be right. For one thing, it’s not taught at watchmaking schools, which generally focus on watch repair rather than watchmaking, much less hand-finishing. That means most people who actually know how to do chamfering by hand learn it at the workshops of manufacturers who still train people to do it. When you remember that it can take ten hours or more to do the chamfering on a single bridge, and that it requires a high level of training and skill, you start to understand why you don’t see it as often as you might think you do.
So how can you tell if the chamfers on a watch movement are actually done by hand? This is the tough part – it can be really, really hard to tell the difference. We often assume that hand-finishing is ubiquitous across all production from a fine watchmaking brand, but is this really the case? If you want to know if your luxury watch is really hand-finished, top to bottom and stem to stern, think about the economics involved.
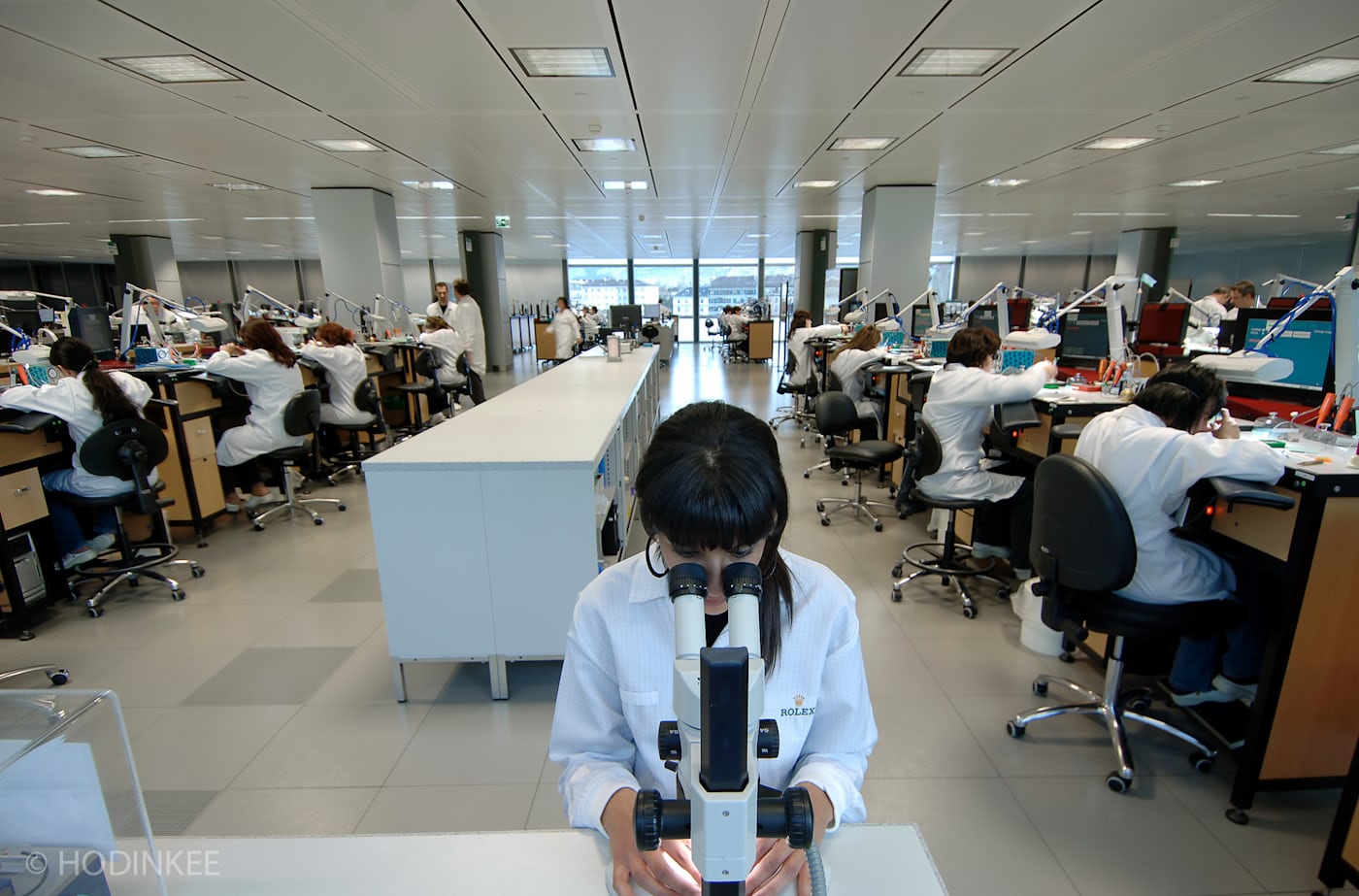
If you’re a luxury watch brand and you’re making, say, sixty to seventy thousand watches a year, the odds are overwhelmingly against hand-chamfering being done on every single bridge in every single watch. For one thing there aren’t enough people who know how to do it to handle that kind of volume and for another, it adds dozens of hours and a lot of uncertainty to the manufacturing process. Where you’ll tend to find the most hand-finishing is on high prestige legacy movements, and very low-production high complications and other “talking pieces.”
Ithink it’s probably worth pointing out that partial hand-finishing or even an absence of hand-finishing in a movement, does not mean that a watch is necessarily poorly finished, and it definitely doesn’t mean it’s a bad watch. Good automated or partially automated finishing is still finishing – it’s not as if you ordered prime rib au jus and got walnut tofu loaf with a side of Vegenaise. The whole history of watchmaking, since the invention of milling machines around two hundred years ago (which were originally invented for the firearms industry, to make guns with interchangeable parts) has been about the pursuit of better mechanical precision.
So the problem isn’t the machines – without them, Rolex couldn’t make a million watches a year that all keep time to within ±2 seconds per day. Actual hand-finishing throughout a movement is a very specific, very time-consuming specialist craft which today is about the preservation of traditional techniques. It’s enormous value-added if you care about that sort of thing, but it doesn’t make a watch any more accurate, reliable, or durable.
“And then, they hand out loupes as gifts – they give you a stick with which to beat them!”
– PHILIPPE DUFOUR
The only issue arises when you think you’re getting something you’re not. Are you getting actual fine watchmaking, or are you getting, essentially, an illustration of fine watchmaking?
Chances are, a company that’s expending a lot of time, energy, and effort on hand-finishing isn’t going to hide their light under a bushel. They’re going to show you. And if they’re not showing you, it is reasonable to ask if they’re actually doing it, and if so, where exactly in their lineup they’re doing it. There is absolutely nothing wrong with some combination of semi-industrial and industrial finishing in mass-produced luxury watch movements but it’s wildly unrealistic to think that luxury watch brands can arbitrarily scale up complete, comprehensive hand-finishing across tens of thousands of calibers.
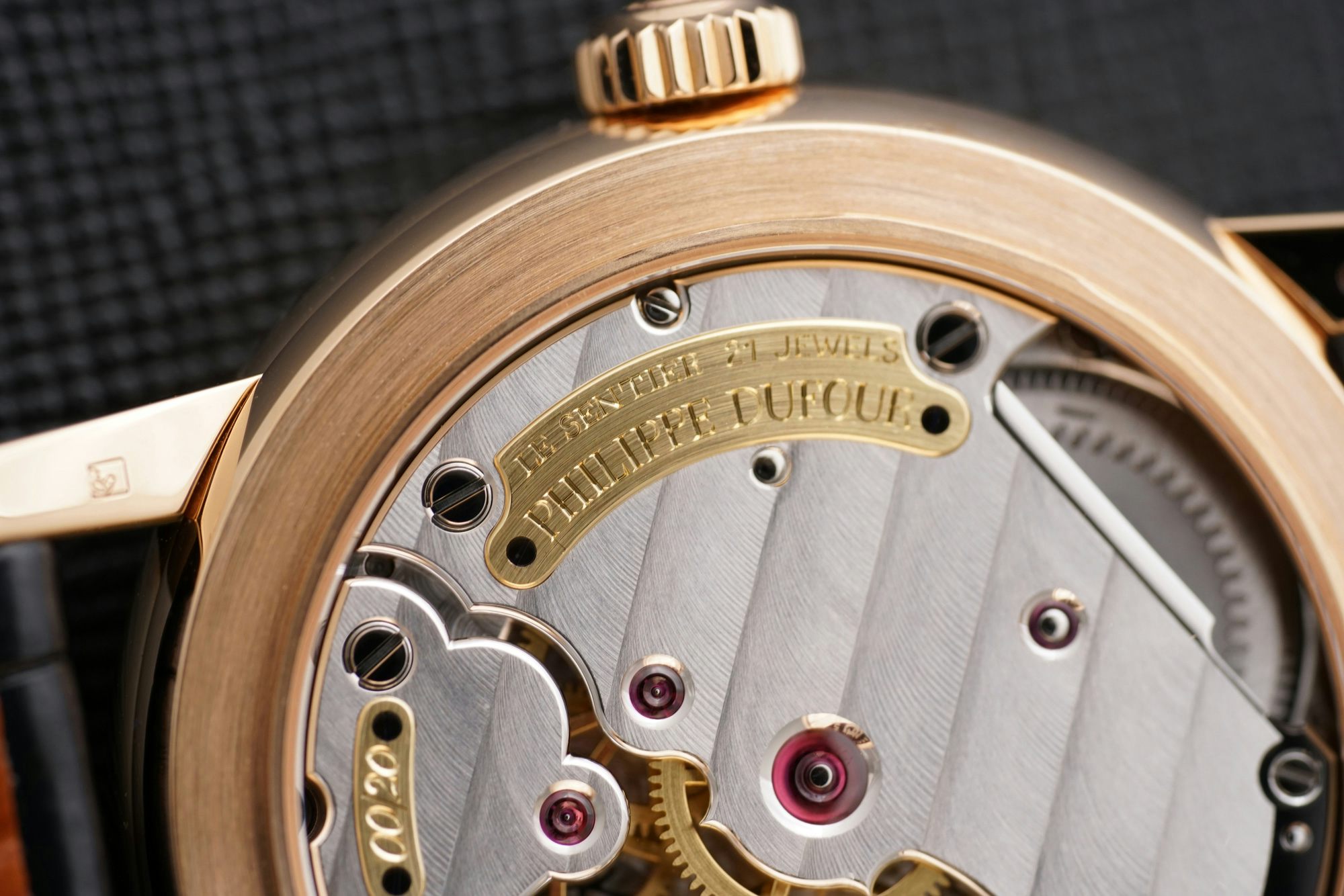
One name that’s virtually synonymous with Swiss hand-finishing is Philippe Dufour, and whenever I think about the subject, I think about a conversation I had with him in his workshop several years ago. He was deploring the drop in standards for finishing in Switzerland, which in his view had deteriorated considerably over his working career. He said that the fine watchmaking brands cut corners on finishing and then, to make matters worse, ” … then they hand out loupes as gifts – they give you a stick with which to beat them!” (It’s worth pointing out that he also happily wears a Rolex GMT-Master as a daily wear watch, so obviously his idea of what constitutes a good watch is not confined to one that is hand-finished throughout. The only watches I’ve ever seen him wear are a Lange Datograph and that GMT-Master … not a bad two-watch collection.)
Hand-finishing includes, but isn’t limited to, polishing flanks, chamfering, black polishing, perlage, polishing screw slots, chamfering screw slots, chamfering the arms of movement wheels … the list goes on and on, and don’t forget that these are all separately learned skills. Doing all of this by hand throughout an entire watch is, for all intents and purposes, simply prohibitively expensive in modern series-produced luxury watchmaking. It’s important to understand, though, that at least from one perspective, it’s this almost impossibly high standard that makes the difference between a good watch – even a great watch – and a watch that’s truly fine in conception and execution all the way through. As the old TV commercial for Zenith electronics used to say, “The quality goes in before the name goes on.”
Get More Articles Like This in Your Inbox
We're constantly creating great content like this. So, why not get it delivered directly to your inbox? By subscribing you agree to our Privacy Policy but you can unsubscribe at any time.